TJU Researchers Improves Nonvolatile Resistive Memory Device
Memristor, the combination of memory and resistance is a memory device that is very promising in the design and preparation of artificial intelligence neural networks. Capable of nonvolatile electrical switch resistance under the application of an external voltage, Memristor is a competitive candidate for next-generation storage technologies due to its high density, low cost, rapid write and read access, low energy operation, high endurance (write cyclability) and retention performance. The performance and reliability of memristors in harsh environments such as high temperatures, organic solvents, etc., is important for memristive devices because their applications can be extended to many promising locations,such as air and space, sea water, biological fluids, military environments, high temperature environments, and industrial gases.
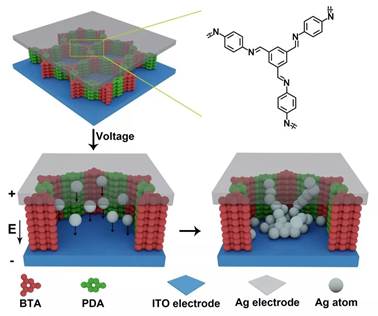
Figure 1. The mechanism of Ag/2DPBTA+PDA/ITO.
Recently, Professors Shengbin Lei and Wenping Hu from Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronics of Tianjin University used BTA (Benzenetricarboxaldehyde) andPDA (p-phenylenediamine) as precursors to synthesize a wafer-scale covalent 2D polymer (2DPBTA+PDA) film with controllable thickness at the air-liquid interface. The synthesized freestanding 2DP films are porous, insulating, and more importantly, covalently linked, which is ideally suited for nonvolatile memristors that use a conductive filament mechanism. Therefore, the device of Ag/2DPBTA+PDA/ITO is fabricated and then electrical properties are studied. This memory device exhibits bipolar non-volatile resistance switching behavior with the switching ratio effectively regulated by the thickness of the two-dimensional polymer from 102to 105. Further research indicates that the device works in the electrochemical metallization process of the active silver (Ag) electrode under voltage. For the first time, this work applies two-dimensional polymers to memristive devices.
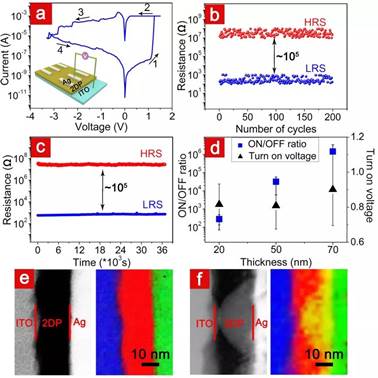
Figure 2. The electrical properties of 2DPBTA+PDA-based memristive devices and mechanism of it.
Benefiting from the high thermal stability and excellent solvent resistance properties of the 2DPBTA+PDAfilms, Ag/2DPBTA+PDA/ITO exhibits good resistance switching behavior after annealing at 300 °C and even in different organic solvents. The stable covalent structure and flexible characteristics make the two-dimensional polymer film a desired material in the preparation of ultra-thin and flexible devices. In this research, the memristors fabricated using 2.6 nm thick 2DPBTA+PDAfilms are the thinnest memristive devices in organic functional layers.
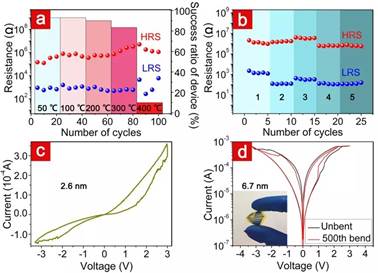
Figure 3. Electrical properties of 2DPBTA+PDA-based memristive devices in harsh environments and their applications in ultra-thin and flexible devices.
The intrinsic flexibility of this film enables its application in flexible devices, which exhibit comparable performance to that on the rigid substrate. This work may provide a good resource for applications in wearable electronics, smart skins, and minimally invasive biomedical devices. The work was published on Advanced Materials under the title "A Robust Nonvolatile Resistive Memory Device Based on a Freestanding Ultrathin 2D Imine Polymer Film".(DOI : 10.1002/adma.201902264)
By the School of Science
Editors: Eva Yin & Doris Harrington

